

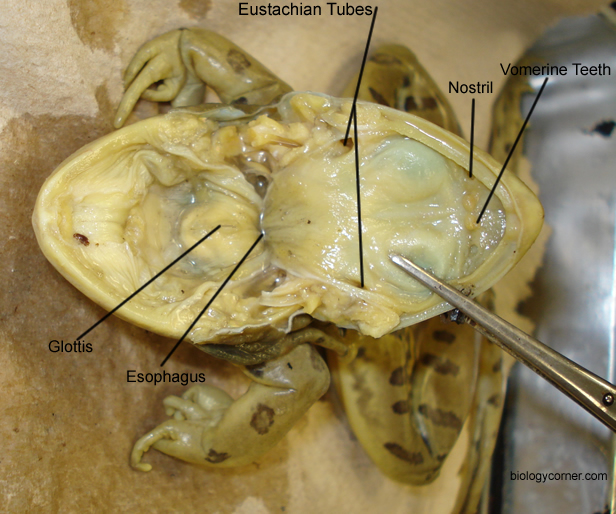

Oxygen-laden blood and oxygen-poor blood containing waste gases are present together in the frog ventricle at all times. In humans, the lower heart chamber is divided into two compartments, the right ventricle and the left ventricle. The frog heart, however, has only one lower chamber, a single ventricle. There are two upper chambers of the heart, the right atrium and the left atrium. The frog heart is the only organ contained within the coelom which has its own protective covering. Internal organs contain smooth muscle tissue. Skeleton-moving muscles are made of skeletal, or “striated,” muscle. The calcaneus in the human skeleton is the heel bone.Īs in other vertebrates, the frog skeleton is moved by muscles. The astragalus corresponds to the human talus. These are the astragalus and the calcaneus. A third division of the frog’s leg consists of two elongated anklebones, or tarsals. In humans and in the frog, the femur is the single upper leg (thigh) bone. Humans have two lower leg bones, the tibia and the fibula. The single “shinbone” is the tibiofibula. The hind legs of the frog are highly specialized for leaping. Both frog and human have one “upper arm” bone, the humerus. Humans have two forearm bones, the radius and the ulna. The frog has one “forearm” bone, the radio-ulna. The shoulders and front legs of the frog are somewhat similar to humman shoulders and arms. The urostyle, or “tail pillar,” is a downward extension of the vertebral column. Only a spikelike bone, the urostyle, remains as evidence that primitive frogs probably had tails. Only nine vertebrae make up the frog’s backbone, or vertebral column. The skull is flat, except for an expanded area that encases the small brain. The frog’s body is supported and protected by a bony framework called the skeleton. All the frog’s internal organs-including the heart, the lungs, and all organs of digestion-are held in this single hollow space. There is no such partition in the frog’s coelom. The human chest is separated from the abdomen by a powerful muscular partition, the diaphragm. The internal organs of humans are housed in one of three distinct hollow cavities-the chest, the abdomen, and the pelvis. The stubby trunk forms walls for a single body cavity, the coelom. A short, almost rigid neck permits only limited head movement. The flat head contains the brain, mouth, eyes, ears, and nose. Copyright Stephen Dalton/Photo ResearchersĪs in other higher vertebrates, the frog body may be divided into a head, a short neck, and a trunk (see Vertebrates).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
